A private Docker registry simplifies managing your application deployments in Kubernetes. Read my tutorial to setup you own private Docker registry in a few minutes.
Kubernetes works with Docker Containers. Docker Containers need to be provided with a Docker registry. If you don’t want to use a public docker registry for publishing the images of your application, you need to setup a private registry.
This article shows you how to deploy a private Docker Registry inside your Kubernetes cluster.
Do I really need a private Docker Registry?
Short Answer: Yes.
Assume you want to deploy the image webpage, here is what happens:
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled <unknown> default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/webpage-5fc78c945d-sl7gx to k3s-node2
Normal Pulling 15s (x2 over 31s) kubelet, k3s-node2 Pulling image "webpage"
Warning Failed 14s (x2 over 31s) kubelet, k3s-node2 Error: ErrImagePull
Warning Failed 14s (x2 over 31s) kubelet, k3s-node2 Failed to pull image "webpage": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = failed to pull and unpack image "docker.io/library/webpage:latest": failed to resolve reference "docker.io/library/webpage:latest": pull access denied, repository does not exist or may require authorization: server message: insufficient_scope: authorization failed
Warning Failed 2s (x2 over 30s) kubelet, k3s-node2 Error: ImagePullBackOff
Normal BackOff 2s (x2 over 30s) kubelet, k3s-node2 Back-off pulling image "webpage"
As you see, in the default configuration, Kubernetes looks for images in the public docker.io registry.
Can you build the images locally, on each of your Kubernetes cluster nodes? Yes, but it does not work because Kubernetes expects to talk to a Docker Registry API.
Therefore: You need to provide the access to a docker registry. If you don’t want to publish the images of your app in a public registry, the only option is to have a private one.
Private Docker Registry
Setting up a private Docker registry requires these essential steps:
- Create a domain and DNS entry
- Install docker registry
- Add TLS certificates
Domain and DNS Entry
The first step will be done with your ISP web interface or similar means. For my domain admantium.com, I created the subdomain docker.adamantium.com. Then I added a DNS entry that points to my Kubernetes cluster.
Install Docker Registry
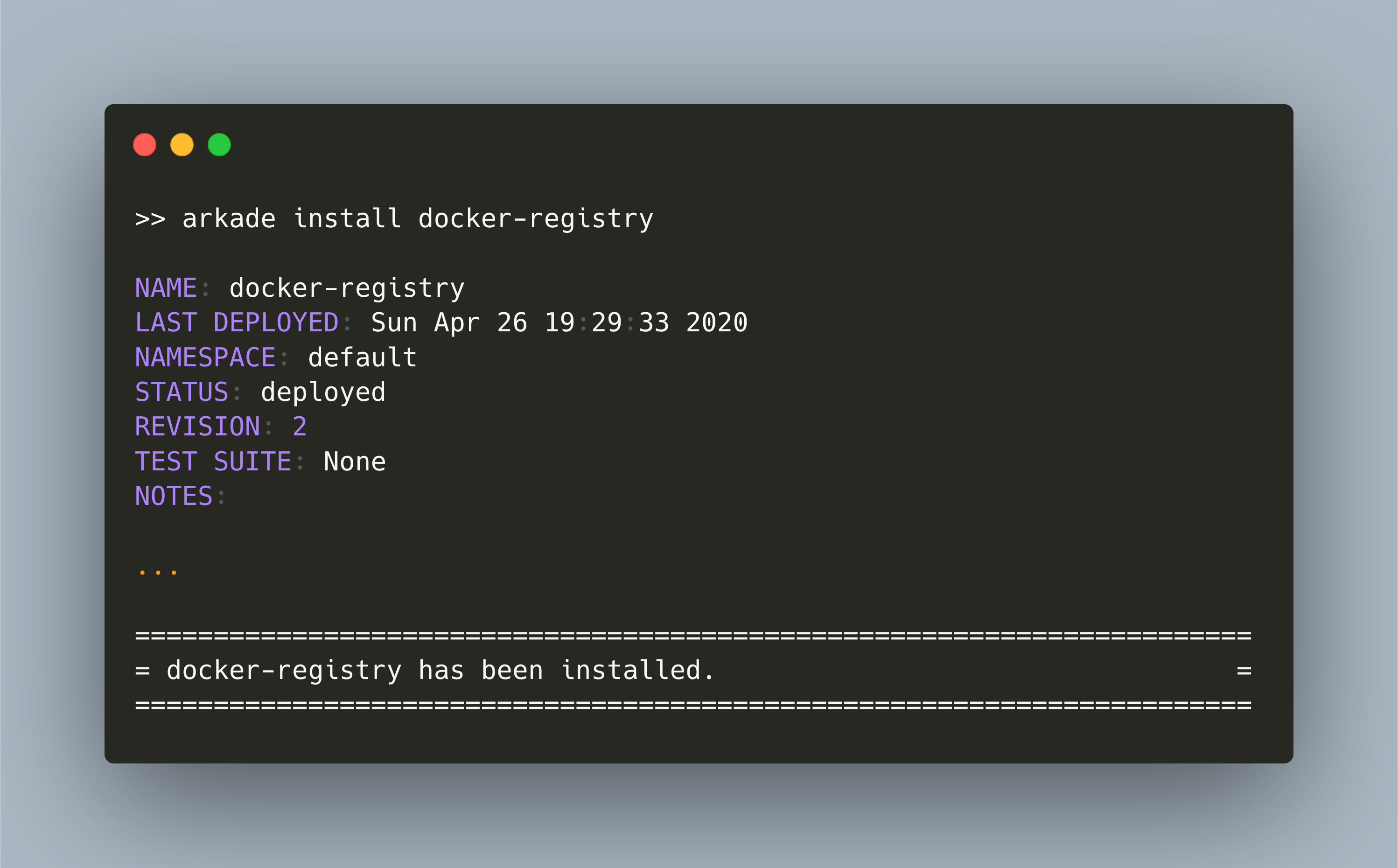
For the second step, we use the arkade helper tool. Execute the following command, then check the output that all goes well.
>> arkade install docker-registry
NAME: docker-registry
LAST DEPLOYED: Sun Apr 26 19:29:33 2020
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 2
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
...
=======================================================================
= docker-registry has been installed. =
=======================================================================
# Find out more at:
# https://github.com/helm/charts/tree/master/stable/registry
Thanks for using arkade!
Registry credentials: USERNAME SECRET
At the bottom of this output, you will see the username and the password. Copy them now.
To access the registry, you need these parameters: domain name, username, password and an e-mail address. Define all of them as environment variables and put them in your .bashrc file.
export DOCKER_REGISTRY=<<domain>>
export DOCKER_USERNAME=<<admin>>
export DOCKER_PASSWORD=<<password>>
export DOCKER_EMAIL=<<email>>
From now on, whenever you execute a docker command, these parameters will be used.
Provide TLS Certificates
The Docker registry should be accessed with a TLS encrypted connection. In my previous article, I explained how to install the cert-manager, a software package that automatically issues and renews certificates.
For the docker registry, we will build upon the cert-manager. With the following command, you will automatically define a new ClusterIssuer, called letsencrypt-prod-registry, and define an Ingress resource which forwards requests of the configured domain name to your Docker registry.
>> arkade install docker-registry-ingress --email $DOCKER_EMAIL --domain $DOCKER_REGISTRY
=======================================================================
= Docker Registry Ingress and cert-manager ClusterIssuer have been installed =
=======================================================================
If you are curious, you can take a look with the following command:
>> kubectl get ingress docker-registry --output=yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-prod-registry
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 200m
spec:
rules:
- host: docker.admantium.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: docker-registry
servicePort: 5000
path: /
tls:
- hosts:
- docker.admantium.com
secretName: docker-registry
status:
loadBalancer:
ingress:
- ip: 49.12.45.26
When the installation is finished, you should check the log files of the cert-manager to see that the TLS certificates are properly installed.
> kubectl logs -n cert-manager deploy/cert-manager
I0502 15:26:54.317163 1 sync.go:379] cert-manager/controller/certificates "level"=0 "msg"="validating existing CSR data" "related_resource_kind"="CertificateRequest" "related_resource_name"="docker-admantium-com-3726166042" "related_resource_namespace"="default" "resource_kind"="Certificate" "resource_name"="docker-admantium-com" "resource_namespace"="default"
I0502 15:26:54.317935 1 sync.go:479] cert-manager/controller/certificates "level"=0 "msg"="CertificateRequest is not in a final state, waiting until CertificateRequest is complete" "related_resource_kind"="CertificateRequest" "related_resource_name"="docker-admantium-com-3726166042" "related_resource_namespace"="default" "resource_kind"="Certificate" "resource_name"="docker-admantium-com" "resource_namespace"="default" "state"="Pending"
I0502 15:26:54.324391 1 controller.go:135] cert-manager/controller/certificates "level"=0 "msg"="finished processing work item" "key"="default/docker-registry"
Test: Pushing Images to Private Docker Registry
If all goes well, we can now access the registry. Execute the following command.
> docker login $DOCKER_REGISTRY --username=$DOCKER_USERNAME --password=$DOCKER_PASSWORD
Login Succeeded
Then, tag your image in this manner: <<DOCKER_REGISTRY>>/<<IMAGE-NAME>>:<<VERSION>>. In my case, I will tag the image as docker.admantium.com/webpage:latest. Then push this image to the registry.
> docker push docker.admantium.com/webpage:latest
The push refers to repository [docker.admantium.com/webpage]
599b6638e2aa: Pushed
81210be95b2f: Pushed
f3629d9fa534: Pushed
403ab6c36d93: Pushed
313be5a92861: Pushed
f6fbf55b4240: Pushing [=============> ] 23.42MB/83.96MB
2fc9f319e2c4: Pushed
de7d7e8f96e8: Pushed
55c928cc6db5: Pushed
e90cdc933987: Pushed
dba921702de8: Pushing [=====> ] 8.229MB/76.92MB
883a1e8c9056: Pushing [==> ] 17.66MB/326MB
1fbb01ef7573: Pushing [==================================================>] 3.584kB
b54ada1169f0: Pushing [==============> ] 2.241MB/7.621MB
0586a03753aa: Waiting
531743b7098c: Waiting
Wonderful, the image can be pushed to the registry. We can now test deploy the webpage image inside the Kubernetes cluster
kb create deployment --image docker.adamantium.com/webpage
But something is wrong ...
>> kb describe pod/webpage-86976f8869-5jgtz
Name: webpage-86976f8869-5jgtz
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Node: k3s-node2/49.12.64.126
Start Time: Sun, 26 Apr 2020 19:57:53 +0200
Labels: app=webpage
pod-template-hash=86976f8869
Annotations: <none>
Status: Pending
...
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled <unknown> default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/test-86976f8869-5jgtz to k3s-node2
Normal Pulling 36s (x3 over 77s) kubelet, k3s-node2 Pulling image "docker.admantium.com/webpage"
Warning Failed 35s (x3 over 75s) kubelet, k3s-node2 Failed to pull image "docker.admantium.com/webpage": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = failed to pull and unpack image "docker.admantium.com/webpage:latest": failed to resolve reference "docker.admantium.com/webpage:latest": unexpected status code [manifests latest]: 401 Unauthorized
Kubernetes is unauthorized to access the registry. So, we need to provide the username and password as a Secrets resource.
Configure a Kubernetes Secrete to Access the Registry
On your client, create the secret as follows.
kubectl create secret docker-registry registry-secret \
--docker-server=$DOCKER_REGISTRY \
--docker-username=$DOCKER_USERNAME \
--docker-password=$DOCKER_PASSWORD \
--docker-email=$DOCKER_EMAIL secret/registry-secret created
Then check this Secret. The information you just entered will be rendered as a JSON file and used by Kubernetes when your registry is accessed.
> kb describe secret registry-secret
Name: registry-secret
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Type: kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson
Data
====
.dockerconfigjson: 166 bytes
Now we need to provide this secret in the deployment file. Create the entry spec.template.spec.imagePullSecrets as shown below.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: webpage
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: webpage
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: webpage
spec:
containers:
- name: webpage
image: docker.admantium.com/webpage:latest
imagePullSecrets:
- name: registry-secret
Now the deployment is successful.
>> kb describe pod/webpage-7b4469547b-cpbrq
Name: webpage-7b4469547b-cpbrq
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Node: k3s-node2/49.12.64.126
Start Time: Sun, 26 Apr 2020 20:43:19 +0200
Labels: app=webpage
pod-template-hash=7b4469547b
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.42.2.151
IPs:
IP: 10.42.2.151
Controlled By: ReplicaSet/webpage-7b4469547b
Containers:
webpage:
Container ID: containerd://a42ac84a8e8fca2e67c5b32a690d00f5b63bd79a71ecd25a5a62764ebb109768
Image: docker.admantium.com/webpage:0.1.0
Image ID: docker.admantium.com/webpage@sha256:1c15180d3d08a8d4c8f5e7f368bbf54a7a33c163cf0aacb4cb60f460aee6e441
Conclusion
In order to use your Kubernetes cluster, access to a private Docker registry is a must. In this article, I showed you how to setup a Docker registry inside you Kubernetes cluster, from which you can then deploy applications. Assuming you have the cert-manager installed (see previous article), you just need to install the docker-registry and docker-registry-ingress packages. You will then have a TLS-encrypted connection to your Docker registry. To push the images to this registry, you need to tag the images appropriately and configure the Docker environment variables on you client correctly. Finally, you need to provide the access credentials to the Docker registry inside your Kubernetes Cluster as a Secret.
With a private Docker registry, you are ready to go and publish your applications.