The Hashicorp Vault secrets management tool comes as an executable binary supporting all major operating systems. The binary itself is a multi-purpose tool, providing several commands to start and configure single vault instances or a cluster of multiple servers, define authentication mechanisms and policies, and configure and work with secret engines.
In a series of blog posts, complete coverage of all CLI commands will be provided. This starting article treats all commands from the intialization group, showing how to start a full Vault server instance, an agent, or a proxy.
The technical context of this article is hashicorp_vault_v1.20, released 2025-06-25. All provided information and command examples should be valid with newer versions too, baring an update of the CLI commands’ syntax.
The background material for this article stems from the official Hashicorp Vault documentation about Vault CLI and subsequent pages, as well as information from the binary itself.
CLI Overview: Basic Commands
As every CLI, the Hashicorp Vault binary, aptly named vault, provides built-in documentation, exposed by passing --help to the root-level or its subcommands. Available commands are printed in a flat list, but they are applicable to different lifecycles of operating and using vault.
Grouping the commands accordingly yields the following structure. The section marked with an at sign is the focus for this article.
- 🌀 Initialization
server: Starts a server processagent: Starts an agent process, a utility to communicate with a vault server to gain access to tokensproxy: Starts a vault proxy process
- Configuration
operator: Cluster management operations, including memberships, encryption and unseal keysplugin: Manage and install additional pluginsread/list: Access stored configuration and secretswrite/patch: Modify or create any datadelete: Delete configuration data or secrets
- Introspection
status: Show status information of the vault serverversion: Shows compact version information and build timestampversion-history: Shows detailed version information about all previously used vault server instancesprint: Detailed view of the vault’s server runtime configurationpath-help: Detailed documentation about API endpointsevents: Subscribe to the event stream of a running vault instancemonitor: Print vault log messagesdebug: Shows debug information of the connected Vault serveraudit: Interact with connected audit devices
- Vault Enterprise
hcp: Operate a managed Hashicorp Vault clusternamespace: Interact with configured namespaces of the cluster
- Authorization
policy: Manage policy definitions that govern all vault operationstokens: General token managementlease: Manage current token leases, including renewal, revocation and TTL modification
- Authentication
auth: Interact with configured authentication optionslogin: Authenticates access to a Vault server
- Secrets Management
secrets: General configuration of secret engineskv: Access to the essential key-value storetransform: Interact with the transform secrets enginetransit: Interact with the Vaults transit secrets engineunwrap: One-time access to arbitrary encrypted datapki: Access the private key infrastructure secrets enginessh: Initiates SSH sessions via the SSH secrets engine
Initialization Commands
This group contains all commands that start a Vault process or a process that communicates transparently with Vault servers are grouped together.
server
This command starts a new vault instance. The most important configuration options can be provided either as flags to this command, or expressed in a configuration file that itself becomes an argument. Defining attributes are these:
address: The local IP address and port to which the vault process is boundca-path: A directory with PEM-encoded certificates that vault uses for encrypting all local trafficclient-cert: One of Vaults authentication mechanisms are client certificates in PEM format. This flag designates a local folder from which the certificates will be loaded.dev: This flag starts a non-production, no-encryption and in-memory only instance of a Vault server
agent
Agent mode provides a process-level communication mode of any server with a Vault instance or cluster. Agents work be being configured with special template formats in which plaintext secrets are rendered. The default options of the server command are available as well, with the following additions:
Subcommands
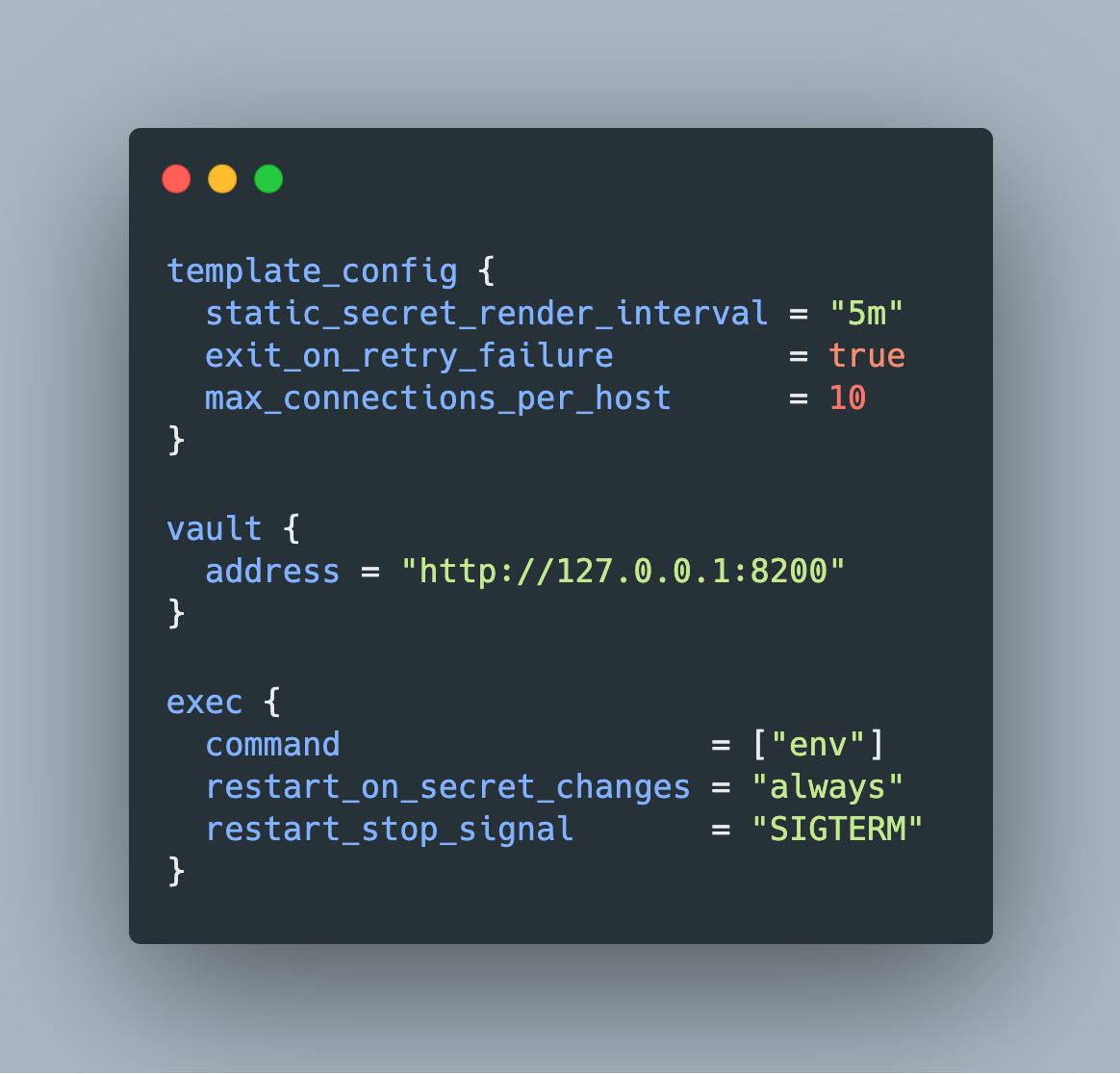
generate-config: As the name suggests, this command generates an agent configuration. Inhashicorp_vault_v1.20, the only option is to append-type="env-template". The resulting file is as follows:
auto_auth {
method {
type = "token_file"
config {
token_file_path = "/home/users/.vault-token"
}
}
}
template_config {
static_secret_render_interval = "5m"
exit_on_retry_failure = true
max_connections_per_host = 10
}
vault {
address = "http://127.0.0.1:8200"
}
exec {
command = ["env"]
restart_on_secret_changes = "always"
restart_stop_signal = "SIGTERM"
}
proxy
This command starts a local process that mimics the API of a Vault instance or cluster. Once authenticated with a Vault, it handles all client requests transparently. An additional benefit is the ability of local client caching, storing responses from authentication methods and leased secrets likewise. To facilitate the usage of a Vault proxy, the initial authentication with vault can be configured as auto authentication. This requires a supported authentication option and a “sink”, a place where the auth information is stored.
No additional subcommands are provided, and as before, the default options of the server command are available too.
Conclusion
The Hashicorp Vault binary is a multipurpose CLI tool. Its more than 30 subcommands can be grouped along different tasks, from which initialization, starting a Vault server process, is the focus of this article. You learned how to start a Vault process that in server mode, as an agent for lightweight Vault interaction that renders secrets to template files, and as a proxy that serves a thin replica of the vault REST API.